Understanding the Difference Between Pulse Induction and VLF Metal Detectors
Share
Understanding the Difference Between Pulse Induction and VLF Metal Detectors
This is a conversation we have every single day in our store. When choosing your first or next Metal detector this is the first decision you need to make.
Which of these 2 technologies is going to suit your metal detecting style, conditions and of course what you want to find.
Remember VLF and Multi Frequency metal Detectors fall into the same category, Pulse induction is entirely different.
Both are Metal Detectors and both can detect gold as it is a metal. Read on and then give us call to clarify any questions you may have.
Metal detectors are widely used in various industries, from treasure hunting, Prospecting and archaeological surveys to security screening at airports. Two commonly employed technologies for metal detection are Pulse Induction (PI) and Very Low Frequency (VLF) detectors.
While both serve the same purpose of detecting metallic objects, they employ different techniques and have distinct advantages and limitations. This article aims to explain the key differences between PI and VLF/Multi frequency metal detectors.
Pulse Induction Metal Detectors: Commonly Referred to as GOLD Detectors
Pulse Induction metal detectors operate by generating short and powerful pulses of current through a coil of wire. These pulses create a magnetic field that quickly collapses. As the magnetic field collapses, any nearby metallic objects will generate their own magnetic fields in response. The detector then measures the duration and intensity of the magnetic field generated by the metal object.
Key Characteristics and Advantages of Pulse Induction Detectors:
- Depth: PI detectors are known for their superior depth capabilities, making them suitable for searching in highly mineralized soils, underwater, and for locating deeply buried objects. Their ability to ignore the mineral content of the soil allows for greater detection depths compared to VLF detectors.
- Discrimination: PI detectors typically lack advanced discrimination features and struggle to distinguish between different types of metals. They tend to respond to all metal targets, which can be advantageous in some situations where you don't want to miss any potential finds.
- Stability: PI detectors are generally more stable in highly mineralized environments where VLF detectors may experience false signals due to the mineral content in the soil.
Very Low Frequency Metal Detectors (Including Multi Frequency): Commonly Referred to as Treasure-Coin-Relic detectors.
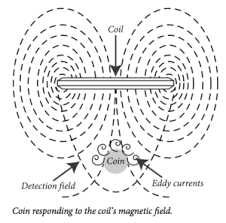
Very Low Frequency metal detectors operate by transmitting a continuous sine wave signal into the ground through the coil. When the transmitted signal encounters a metallic object, it creates eddy currents within the metal, which in turn generate a magnetic field. This magnetic field disrupts the frequency of the detector's coil, resulting in an audible response.
Key Characteristics and Advantages of VLF Detectors:
- Target Identification: VLF detectors offer advanced discrimination features, allowing users to identify and discriminate between different types of metals. This feature is useful in scenarios where you want to filter out unwanted objects, such as nails or aluminium foil, and focus on valuable targets like gold or coins.
- Sensitivity: VLF detectors are generally more sensitive to small and shallow targets, making them suitable for tasks such as coin shooting or relic hunting in less mineralized soils.
- Ground Balance: VLF detectors often have manual or automatic ground balance settings, allowing users to adjust the detector's sensitivity to mineralization. This feature helps in reducing false signals caused by mineral content in the soil.
Choosing the Right Detector: Deciding between a PI or VLF metal detector depends on various factors such as the intended use, search environment, target type, and personal preferences. If you prioritize depth and stability in highly mineralized areas or underwater, a PI detector may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you require target identification capabilities and plan to search in less mineralized soils, a VLF detector may be the better choice.
Conclusion: Pulse Induction and Very Low Frequency metal detectors employ different technologies and offer distinct advantages for metal detection. While PI detectors excel in depth and stability in mineralized environments, VLF detectors provide target identification and sensitivity to small and shallow targets. Understanding the differences between these two types of metal detectors will help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and search conditions.
We specialise in getting you into the right metal detector for your needs while keeping your budget in mind.
Give us a call and let us answer the questions you will inevitably have about which model to choose.
Thanks for reading